Treatment of pulmonary embolism (PE)

Suddenly developed shortness of breath, dizziness, pale skin, chest pain symptoms in themselves alarming. What could it be - attack of a stenocardia, hypertonic crisis, an attack of low back pain?
Possible. But among the suspected diagnoses should be another threatening and require emergency medical care, pulmonary embolism (PE).
What is PE and why it develops
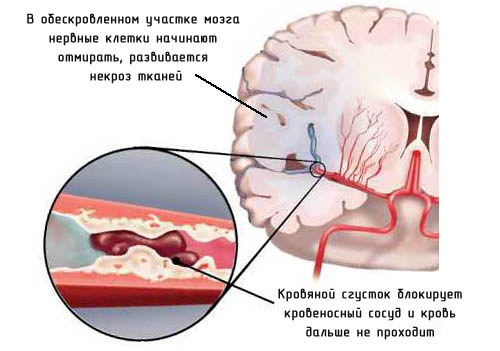
Pulmonary embolism - blockage of the lumen of the pulmonary artery floating (movable) by a blood clot. Embolism may also be a relatively rare condition caused by a hit to the arteries (air embolism), foreign body, fat, tumor cells, or amniotic fluid during pathological delivery.
Most often the culprits in the blockage of the pulmonary artery clots become detached - one or several. Their size and number determine the severity of symptoms and the outcome of the pathology: in some cases, people may not even pay attention to its state in the absence of or mild symptoms, in others - to be in intensive care or even suddenly die.
To areas of risk for the probability of blood clots include:
- Deep vascular of lower extremities;
- The veins of the pelvis and abdomen;
- Vessels of the right chamber of the heart;
- Veins of hands.
To ensure that blood vessel has a blood clot requires several conditions: concentration of the blood and its stagnation in combination with damage to the wall of the vein or artery (the Virchow triad).
In turn, the above conditions do not occur in a vacuum: they are the result of deep disorders in the circulation system of blood, its coagulation, and also in the functional state of blood vascular.
What are the reasons?

The variety of factors that can cause thrombus formation, makes the experts so far to lead discussions on the starting mechanism of development of pulmonary embolism, although the main causes of occlusion of veins pulmonary artery is considered to be the following:
- Congenital and rheumatic heart diseases;
- Urological diseases;
- Oncopathology in any of the organs;
- Thrombophlebitis and thrombosis of the legs.
Pulmonary embolism often develops as a complication of already existing vascular or oncological diseases, but can also occur in completely healthy people - for example, those who are forced to spend a lot of time in travel.
In healthy vascular spending long periods in airplane seat causes poor circulation in the vascular of the legs and pelvis - stagnation and blood clotting. Thoughvery rarely, a clot may form and to begin the fatal journey " even those who do not suffer with varicose veins, no problems with blood pressure or with heart.
There is another category of people with high risk of thromboembolism: patients after injuries (most often hip fracture), strokes and heart attacks - that is, those who have to observe strict bed rest. Poor care exacerbate the situation: in immobilized patients slows blood flow, which ultimately creates the preconditions for the formation of clots in blood vascular.
Found pathology in obstetric practice. Pulmonary embolism as severe complications of childbirth is most likely in women having a history of:
- Varicose veins of the legs;
- Damage veins of the small pelvis;
- Obesity;
- More than four previous births;
- Preeclampsia.
Increase the risk of pulmonary embolism caesarean section for emergency indications, birth to 36 weeks sepsis, which developed as a result of purulent lesions of tissues, long immobilization, for injuries are shown, as well as flights lasting more than six hours before the birth.
The dehydration of the body, often beginning when unrestrained vomiting or uncontrolled passion laxatives to combat so common in pregnant women constipation leads to thickening of the blood, which can cause the formation of clots in blood vascular.
Although extremely rare, but pulmonary embolism is diagnosed even in infants the causes of this phenomenon can be explained by the deep prematurity of the fetus, presence of congenital vascular and heart pathologies.
Thus, pulmonary embolism may develop at almost any age - would be the prerequisites for this.
Classification of pulmonary embolism
As mentioned above, clogging of the pulmonary artery or its branches can blood clots of different sizes, different may be their number. The greatest danger represent blood clots attached to the vessel wall with only one hand.

Off the clot when you cough, sudden movements, straining. Detached clot is the Vena cava, the right atrium passes through the right ventricle of the heart and into the pulmonary artery.
There it can remain whole or be broken on the vessel wall: this event occurs thromboembolism small branches of the pulmonary artery because of the size of the pieces of the clot is quite enough for thrombosis of vascular of small diameter.
If a lot of blood clots, blockage of their lumen of the artery leads to increased pressure in the pulmonary vascular and development of heart failure by increasingthe load on the right ventricle - this phenomenon is known as an acute pulmonary heart, one of the obvious signs of a massive pulmonary embolism.
The severity of embolism and the patient depends on the extent of vascular lesions.
There are the following degrees of pathology:
- Massive;
- Submissively;
- Small.
Massive pulmonary embolism means that affected more than half of the vascular. Under submassive pulmonary embolism thrombosis is understood a third to a half of the large and small vascular. Small thromboembolism - a condition that affects less than one third of pulmonary vascular.
The clinical picture
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism can have different degrees of intensity: in some cases, it passes almost unnoticed, in others it has a rapid onset and a disastrous final few minutes.
The symptoms that lead a doctor to suspect the beginning of a pulmonary embolism include:
- Shortness of breath;
- Tachycardia (significant acceleration of the cardiac rhythm);
- Chest pain;
- The appearance of blood in sputum when coughing;
- Temperature rise;
- Moist rales;
- Blueness of lips (cyanosis);
- Coughing;
- Pleural RUB;
- A sharp and rapid drop in blood pressure (collapse).

Symptoms of pathology in a certain way combined with each other, forming a whole symptoms (syndromes) that can manifest in various degrees of thromboembolism.
So, for small and submassive thromboembolism in pulmonary vascular typical of pulmonary-pleural syndrome: patients develop shortness of breath, pain in the lower parts of the chest, cough with phlegm or without.
Massive embolism occurs with severe cardiac syndrome: chest pain type of angina, a sharp and rapid drop in pressure, after which comes the collapse. On the neck of the patient you can see the swollen veins.
Arrived on-call doctors say these patients reinforced the cardiac impulse, positive venous pulse, accent of the second tone on pulmonary artery, increase in blood pressure in the right atrium (CVP).
Pulmonary embolism in the elderly is often accompanied by cerebral syndrome - loss of consciousness, paralysis, convulsions.
All of these syndromes may be combined with each other.
Just in time to see the problem?
The diversity of symptoms and their combinations, and their similarity with other manifestations of vascular and cardiac diseases considerably difficult to diagnose, in many cases, leads to fatal outcome.

What is customary to differentiate between thromboembolism? It is necessary to exclude diseases with similar symptoms: heart attackinfarction and pneumonia.
Diagnostics at suspicion on thromboembolism of the pulmonary vascular must be fast and accurate in time to take action and minimize the serious consequences of pulmonary embolism.
For this purpose, hardware methods, including:
- Computed tomography;
- Perfusion scintigraphy;
- Selective angiography.
ECG and x-rays have a smaller potential in the diagnosis of thromboembolism of the pulmonary vascular, therefore, the data obtained in the course of these types of studies is restricted.
Computed tomography (CT) can reliably diagnose not only the pulmonary embolism and pulmonary infarction is one of the most severe consequences of thrombosis of the body.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) - also a very reliable method of research which can be used even for the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism for pregnant women due to the lack of radiation.
Perfusion scintigraphy is non-invasive and relatively cheap diagnostic method, giving the opportunity to more than 90 percent to determine the likelihood of embolism.
Selective angiography reveals the unconditional signs of the development of pulmonary embolism. It is intended not only confirmation of the clinical diagnosis, but also identify the place of thrombosis, as well as monitoring of blood flow in the pulmonary circulation.
During the procedure, angiography can be a blood clot beirout by means of a catheter, and then to start therapy: this technique allows to obtain reliable criteria on which to assess the effectiveness of the treatment.
Qualitative diagnosis of patients with signs of thromboembolism of the pulmonary vascular is impossible without the removal of the angiographic index of severity. This figure is calculated on a scale, indicating the degree of vascular lesion in embolism. Assessed the level of insufficiency of blood supply, which in medicine is called a perfusion deficit:
- Index in 16 points and below, perfusion deficit in the 29% corresponds to a mild degree of thromboembolism;
- Index 17-21 score and perfusion deficit in 30-44 percent indicates the average degree of circulatory disorders of the lungs;
- Index 22-26 points and a deficit of perfusion in the 45-59 percent indicators of severe lesions of the blood vascular of the lungs;
- Extremely heavy the degree of pathology is estimated at 27 or more points of the angiographic index of severity and more than 60 per cent of the perfusion deficit.
Pulmonary embolism is difficult to diagnose not only because of the diversity inherent in her symptoms and their deceptions.The problem is that the survey should be carried out as quickly as possible, because the patient's condition may deteriorate directly into the eyes due to repeated thrombosis of the vascular of the lungs at the slightest load.
For this reason, diagnostics at suspicion on thromboembolism is often combined with therapeutic interventions: before the examination the patient is administered an intravenous dose of heparin is 10-15 thousand UNITS, and then is conservative or operative therapy.
How to treat?
Methods of treatment, in contrast to the methods of diagnosis of pulmonary embolism, not particularly diverse and consist of emergency measures aimed at saving the lives of patients and restoration of patency of blood vascular.
For this purpose, both operational and conservative treatment methods.
Surgical treatment
Pulmonary embolism is a disease, the success of the therapy which depends on the massiveness of thrombosis and the overall severity of patients.
Previously used methods for removal of emboli from the affected vascular (e.g., the operation of Trendelenburg) are now used with caution because of the high mortality.
Experts prefer the intravascular catheter embolectomy, which allows to remove the clot through the chambers of the heart and blood vascular. Such operation is considered to be more gentle.
Conservative treatment
Conservative therapy is used to liquefy (lysis) of blood clots in the affected blood vascular and restore blood flow in them.
For this purpose, preparations-fibrinolytic, anticoagulants direct and indirect action. Fibrinolitiki contribute to the thinning of blood clots, and anticoagulants prevent blood clots and re-thrombosis of pulmonary vascular.
Combination therapy in pulmonary embolism is also aimed at the normalization of cardiac activity, the removal of spasm, correction of metabolism. In the course of treatment apply anti-shock, anti-inflammatory, expectorant drugs, analgesics.
All drugs are administered via a nasal cannula, intravenous drip. Some of the drugs patients can receive through a catheter inserted into the pulmonary artery.
Small and submissiona degree of PE have a good prognosis if diagnosis and treatment were carried out promptly and in full. Massive pulmonary embolism results in the quick death of the sick, if them in time not to enter fibrinolytic or not to provide surgical care.
We also recommend to read the materials on the website, what are the risks of deep vein thrombosis.